The purpose of the mounting apparatus designed by Esen Plastik is to easy assemble the corrugated pipes with the socket and/or muff. For this purpose, it is to prevent damages and problems in the sockets and muffs due to the use of earth digger and construction machines.
How Should Trench Section Be for HDPE Corrugated Pipe?
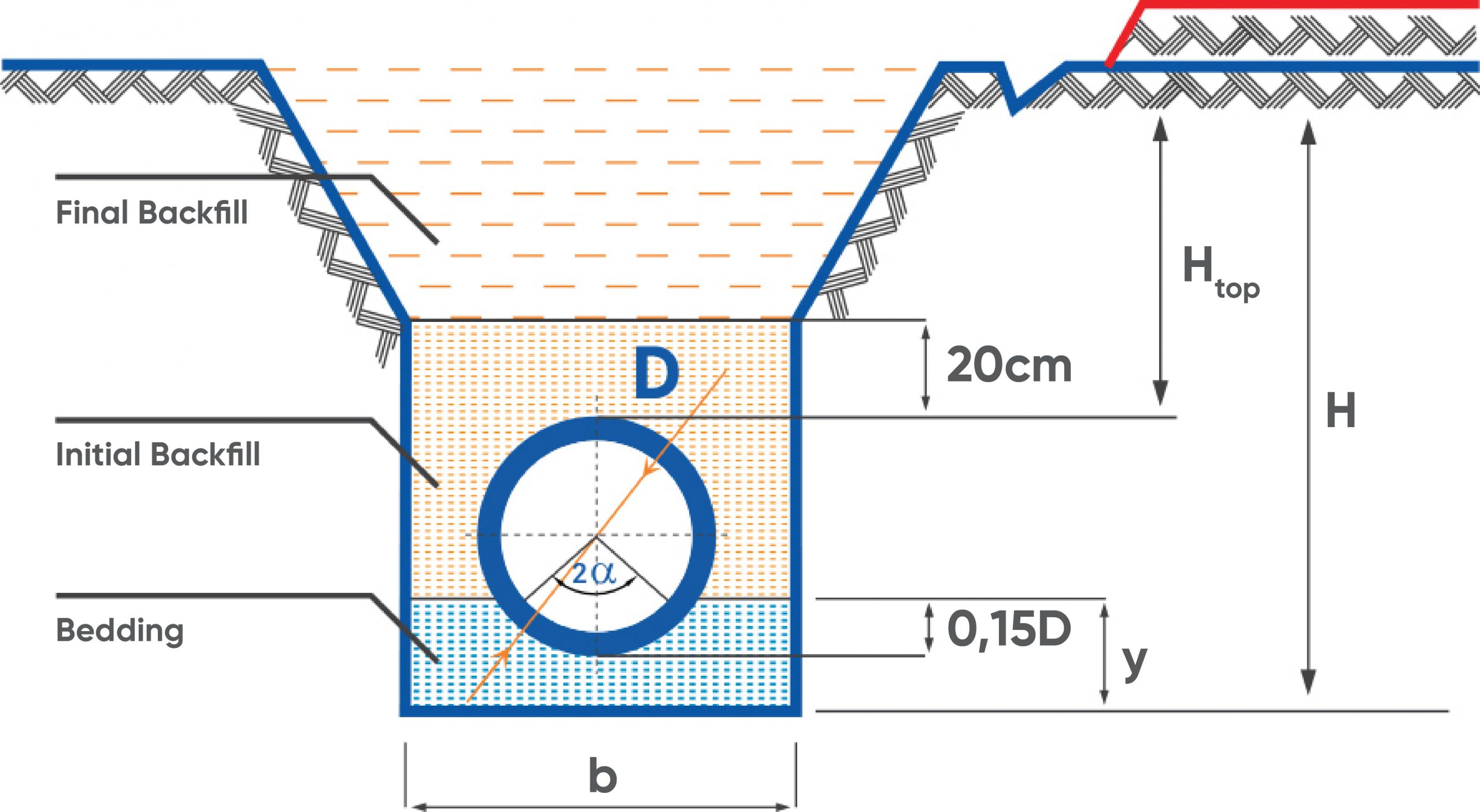
-
FINAL BACKFILL: Uncompacted soil filling. (Except for road crossings)
-
INITIAL BACKFILL: Compressed earth filling, free from hard objects
-
BEDDING: Compressed sand
-
H: Trench Depth (cm)
-
Height top: The distance between the pipe top level and the ground (cm)
-
b: Trench Width (cm)
-
Y: Cushion Layer Height (cm)
-
D: Pipe Outer Diameter (mm)
-
2 : Bedding Angle in Degrees
What Are The General Laying Rules for HDPE Corrugated Pipe?
Correct assembly and proper bedding prolongs pipe life. You can consult the ESEN Project Support Team in all matters related to pipe laying. ESEN Project Support Team will be pleased to provide the required trainings at our factory or at your construction site.
-
Damaged pipes should never be used.
- Groundwater should not be in the canal. If there is any, it should be discharged out of the canal with the means of a pump.
-
Can be used ATV-A127 and EN 805 standards for Pipe Laying.
-
Canal / Trench base is opened according to the land level, should be free from sharp objects.
-
To create the cushioning layer , It should be compacted and spread cushioning material (sand) 95%.
-
To create the shirt Layer, soil material free from sharp objects should be poured at each 30 cm and compressed by 95%. This process should be repeated by every 30 cm.
-
After the shirt layer compression process is finished, soil filling is used to close the canal/trench.
Collapse Pressure Calculations
Pipes laid under the ground are exposed some burdens of outside the soil load. These can be loads that occur directly in the laying of pipes to the sea, such as sea discharge, or there may be extra loads created by groundwater when the pipe is laid under the ground. Apart from these loads, pipes are intertwined by using the shirting method, Lining concrete is made to fill the gap between pipes or in projects where there will be excessive stress, such as additional loads in vacuum-operated pipes for suction purposes, it is necessary to calculate stability (collapse).
Stability (collapse) pressure calculation for HDPE Corrugated Pipes:


ESEN HDPE Corrugated Pipe Connection Apparatus

Attaching / Detaching Arm
This piece is designed in 2 sets. 1. set for 300 mm –600 mm diameter pipe, The second set includes corrugated pipes between 800 mm and 1000mm diameters. It is used for assembling or disassembling.
In diameter changes, the width of the arm will be inserted or removed according to the size of the sockets by means of butterfly head bolts that can be increased or decreased.
Clamp Parts
These parts are placed on the pipes from both sides of the sockets so that corrugated pipes can be assembled or disassembled. It is used for which diameter is shown on the clamps. (The clamps in the picture are suitable for a 400mm Corrugated Pipe.)
Attaching and Detaching Iron Plates
Attaching Iron Plates is used during the joining process of Corrugated Pipe.
Detaching Iron Plates is used during dismantling of Corrugated Pipe.
Connection Process of Corrugated Pipes
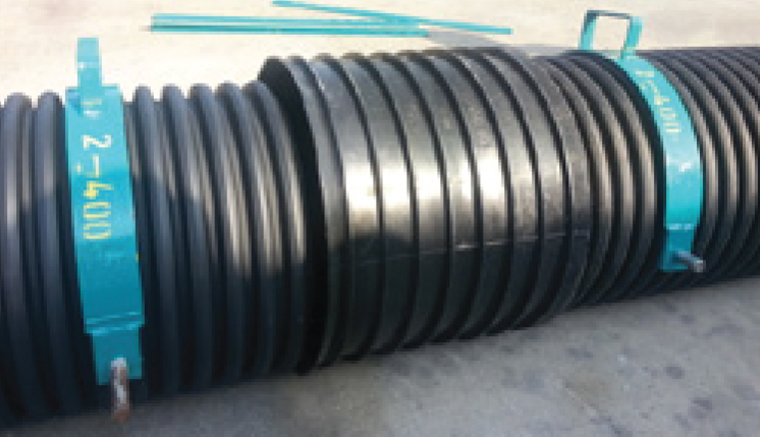

1) The clamp pieces number 2 are placed on the corrugated pipes that will join and have their seals installed.
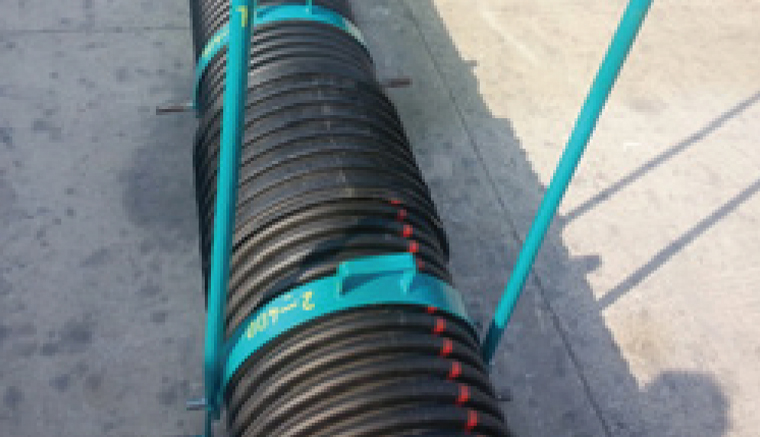

2) Attaching / Detaching Arm width ( relevant diameter ) is adjusted according to the corrugated pipe and this arm is inserted into the pins on both sides of the clamp.
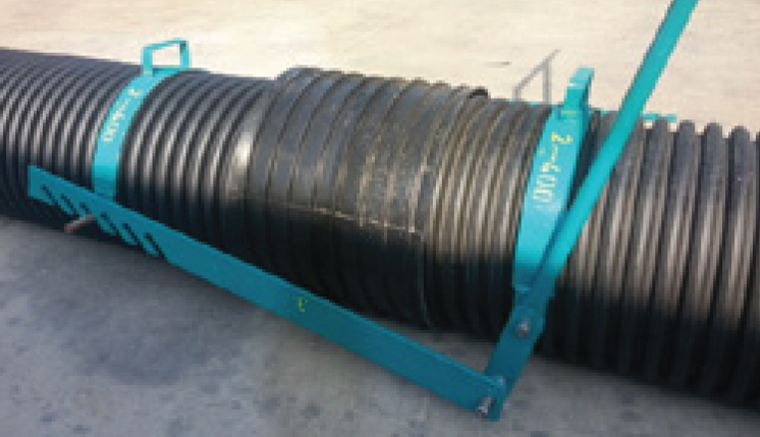

3) Perforated sides of attachment Iron Plates are inserted from both sides to the pins on the bottom of the Attaching / Detaching Arm. The slotted sides of the attachment Iron Plates are placed to the pins on both sides of the other clamp part.
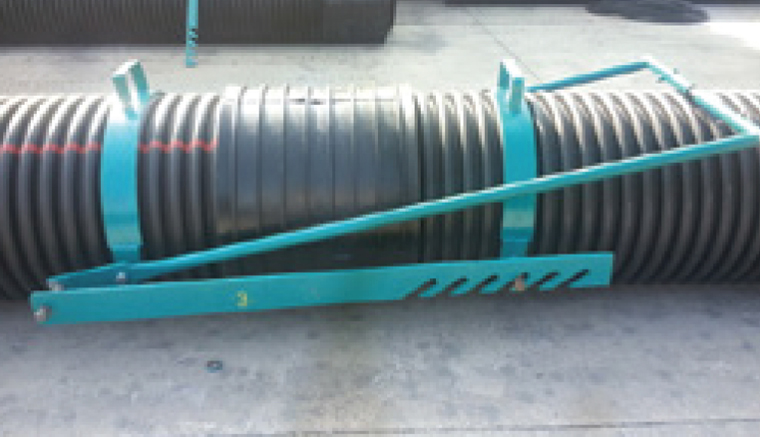

4) By moving the Attaching / Detaching arm forward, the pipes are moved towards each other. If the pipes are not joined, the arm is pulled back and then moved forward again to join the pipes.









